It’s now been more than a year (October 2012) since Google launched Google Tag Manager – its new tag management tool. More and more companies are signing up to it, because it can be used to insert a high number of tags without the need to edit any website code. Without any development expertise, you can now insert Google Analytics tracking code into your website, track events or insert remarketing tags in under 5 minutes!

How does Google Tag Manager work?
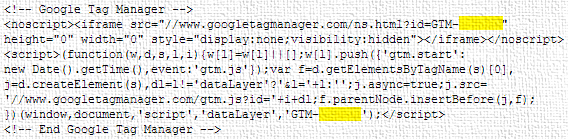
Using Google Tag Manager involves inserting a container snippet into your website. This is just a few lines of code that will fire as many tags as you wish on whichever pages you want.
When you create your Google Tag Manager account, you will receive a container ID and a code snippet as shown in the example below:
The advantage is that you only need to insert this container once on the pages of your website (just after the openingtag). You can then manage all of your tags from the Google Tag Manager interface, without having to access your website’s back-office module every time you make a change.
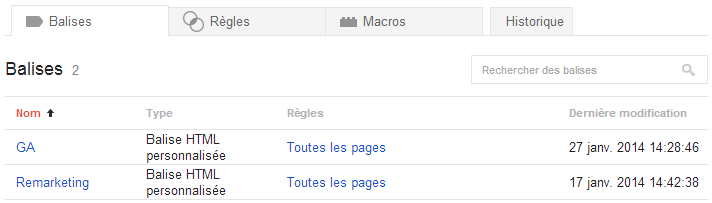
Google Tag Manager features 3 important components: tags, rules and macros.
Tags:
This is where you will find all of the tags which will fire on predefined pages on your website. In the following example, Google Analytics tracking tags and Remarketing tags are fired on all of the site’s pages:
Rules and macros:
Rules and macros are parameters which govern whether or not the various tags that you have implemented are fired. They can be configured so that tags are fired on certain pages only, or when a user performs a particular action (such as submitting a form, adding an item to a basket, etc.).
In this example, we want to create a rule which will fire a particular tag on the “products” page only:
Rules and macros fire tags based on completely customisable events, such as the URL of the user’s referring site, or even their cookie.
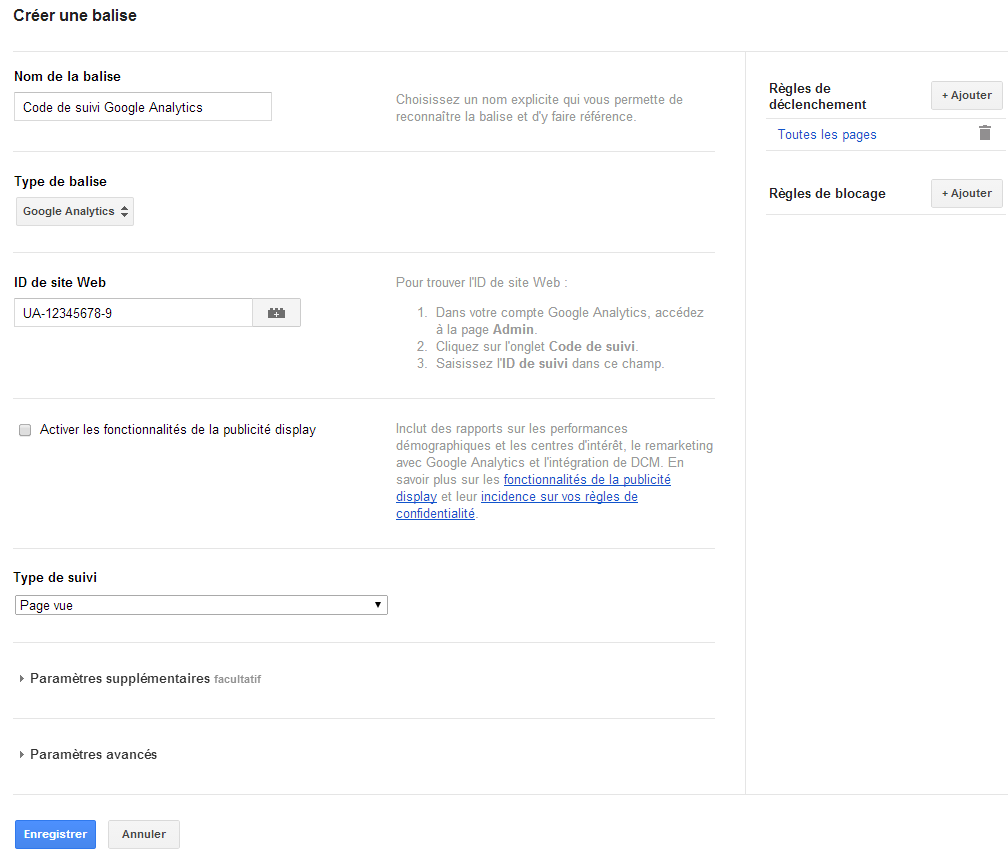
Tag example: How can Analytics tracking code be added via Google Tag Manager?
There’s nothing to it. First, you just have to create a new tag. From the “tag type” drop-down menu, select Google Analytics. You then have to provide the Analytics tracking ID that you will find in the “admin” tab of your Google Analytics account (UA-xxxx…).
On the right, specify the conditions under which you want this tracking tag to be fired (in this example, on all of the site’s pages). Then save your tag.
To finish, you need to create a new version of the container (in the top right-hand corner of the GTM interface). It is advisable to test this version before publishing it on your website. To do this, go to the “Versions” tab in the left-hand menu and select the most recent version of your container. Select “preview and debug” in order to check that your tag works properly on your site. You can then “publish” the most recent version of your container. It is important to follow all of the steps described above every time you make changes to your container.
Google Tag Manager for mobile applications
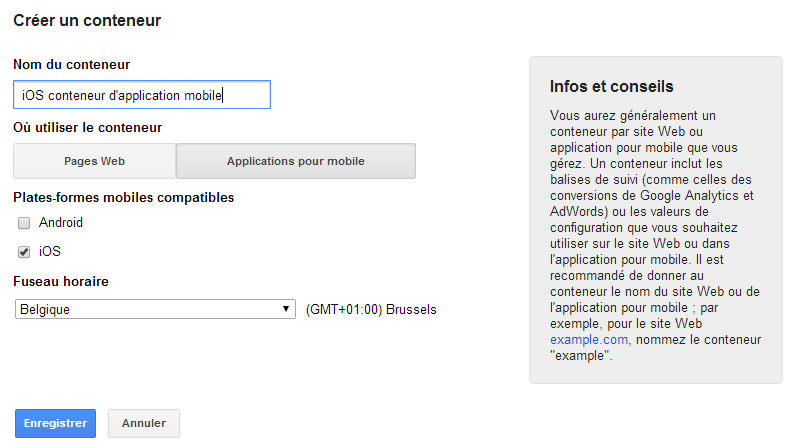
As well as managing tags on your website, you can also use Google Tag Manager to manage all the tags on your mobile applications!
To do this, all you have to do is create a new container for each application:
Google Tag Manager will then provide you with customised SDKs that you will then need to install directly into your application. Once you’ve done this, you can manage all of your tags from the Google Tag Manager interface, exactly as you would for your website.
Tips: a few benefits of Google Tag Manager
- You can easily manage all of your remarketing tags. Easier integration for Adwords, AdRoll and Turn.
- You can track all of your events easily. Without making any changes to your code, you can now monitor clicks on links, form submissions, contact requests or items added to a basket using “event listener” tags.
- Google Tag Manager also integrates the tags of many external tools, such as ClickTale, ComScore, Bizo, Media6Degrees, AdAdvisor, Marin Software, etc.
- Easier migration to Universal Analytics – you no longer need to make changes to your code directly on your website.
- More than one person can manage your Google Tag Manager account – administrators can be added using just their email addresses.
- You can keep a history of all the versions of your container and you can restore a previous version in the event of a problem.
- …
Need help implementing Google Tag Manager or just a few tips about using Web Analytics? Please feel free tocontact us!!